Published September 12, 2023 Welcome! Today, my goal is to help you understand Form W-9 and explore everything we need to know about it. Whether you’re a business owner, freelancer, or just curious about tax forms, understanding Form W-9 is essential in the world of accounting. So, let’s dive right in!
Table of Contents
Overview of Form W-9
Importance of Form W-9 in Accounting
Purpose of the Post
Definition and Function of Form W-9
Who Needs to Complete Form W-9?
Key Components of Form W-9
The Information Requested on Form W-9
Personal Information
Name and Business Name
Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN)
Address
Certification Section
Certification of Correct TIN
Exemptions from Backup Withholding
Scenarios Requiring Form W-9
Independent Contractors
Freelancers and Self-Employed Individuals
Partnerships and LLCs
S-Corporations and C-Corporations
Obtaining and Submitting Form W-9
Methods of Obtaining Form W-9
Completing Form W-9
Submitting Form W-9 to Requesting Parties
Implications of Form W-9 in Accounting Role of Form W-9 in Income Reporting Tax Reporting and Compliance Implications for Requesting Parties Common Misconceptions about Form W-9
Myth: Form W-9 Determines Employment Status
Myth: Form W-9 Initiates Tax Withholding
Myth: Form W-9 is Only Required for U.S. Citizens
Form W-9 vs. Form W-4: Understanding the Difference
Purpose and Usage of Form W-4
Key Differences Between Form W-9 and Form W-4
Situations Requiring Both Forms
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Who Can Request Form W-9?
Is Form W-9 Required for Foreign Contractors?
What Happens if I Refuse to Complete Form W-9?
Can I Amend or Update Form W-9?
Tips for Accurate Form W-9 Completion Double-Checking Information Maintaining Up-to-Date Records Seeking Professional Guidance Appendices
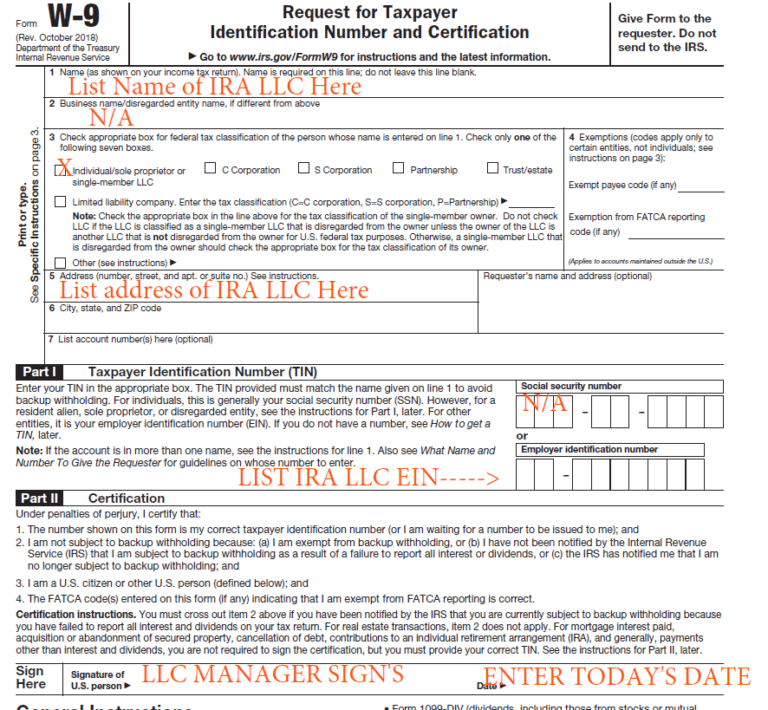
Appendix A: Sample Form W-9
Appendix B: IRS Resources for Form W-9
Appendix C: Glossary of Terms
Introduction
First, let’s get acquainted with Form W-9. We’ll begin by giving an overview of what it is, why it holds importance in accounting, and the purpose behind this blog.
What is Form W-9?
Form W-9 is a tax form issued by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in the United States. It serves as a request for taxpayer identification information from individuals or entities that may be required to file an information return with the IRS. Essentially, it’s a way for the IRS to collect the necessary details to ensure accurate reporting of income.
Importance in Accounting:
Form W-9 plays a crucial role in accounting, particularly when it comes to income reporting and tax compliance. When businesses or organizations pay certain types of income, they are required to gather the necessary taxpayer information from the payee. This helps the IRS track income, ensure proper tax reporting, and prevent tax evasion.
Purpose of this Post:
The purpose of this post is to demystify Form W-9 and provide you with a comprehensive understanding of its various aspects. I want to equip you with the knowledge to navigate the world of accounting and taxation confidently. By delving into the details of Form W-9, I aim to empower you to accurately complete the form, comply with tax regulations, and navigate potential scenarios that require its usage.
Whether you’re a business owner, freelancer, or simply curious about tax forms, understanding Form W-9 is essential. It not only helps you fulfill your own tax obligations but also ensures that you provide accurate information to the entities requesting it from you.
Through this post, we’ll explore the purpose and function of Form W-9, the information it requests, scenarios where it is necessary, its implications in accounting, common misconceptions, and much more. By the end, we’ll have a comprehensive understanding of Form W-9 and be well-prepared to handle its requirements.
So, let’s embark on this journey together and demystify Form W-9, empowering ourselves with the knowledge to navigate the intricacies of tax compliance and accounting. Let’s get started!
Understanding Form W-9
To comprehend Form W-9 fully, we need to delve deeper. We’ll explore its definition, its function, and who exactly needs to complete this form. Additionally, we’ll break down the key components of Form W-9 to ensure we have a solid understanding.
Great! Now let’s dive into understanding Form W-9 in more detail. We’ll explore its definition, its function, who needs to complete it, and the key components that make up this important tax form. So, let’s get started!
Definition and Function of Form W-9
Form W-9 is a tax form issued by the IRS, and its primary function is to collect taxpayer identification information. When a business or organization needs to report certain types of payments to the IRS, they rely on the information provided on Form W-9 to ensure accurate reporting. This form serves as a request for the recipient’s taxpayer identification number (TIN) and other necessary details.
In simpler terms, Form W-9 acts as a tool to gather the information needed to accurately report income and ensure tax compliance. It helps the IRS track and match income reported by payers with the income reported by recipients, thus maintaining the integrity of the tax system.
Who Needs to Complete Form W-9?
Let’s explore when and how to use Form W-9. We’ll delve into various scenarios that require Form W-9, such as independent contractors, freelancers, partnerships, LLCs, S-Corporations, and C-Corporations. We’ll also cover the methods of obtaining Form W-9, completing the form accurately, and submitting it to the requesting parties.
Scenarios Requiring Form W-9
-
- Independent Contractors: If we provide services as an independent contractor, our clients may request us to complete Form W-9. This is because they need our taxpayer identification information to accurately report the payments they made to us. Whether we’re consultants, freelance writers, or gig workers, it’s important to be aware of this requirement.
-
- Freelancers and Self-Employed Individuals: Similar to independent contractors, freelancers, and self-employed individuals often find themselves in situations where they are asked to complete Form W-9. This can occur when we receive payments for our services or when we enter into business relationships with other entities.
-
- Partnerships and LLCs: Partnerships and Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) may require their partners or members to complete Form W-9. This allows the partnership or LLC to report the income distributed to its partners or members accurately. If we’re part of a partnership or LLC, our entity may request us to provide a completed Form W-9.
-
- S-Corporations and C-Corporations: S-Corporations and C-Corporations often need to collect Form W-9s from individuals or entities to whom they make payments. This helps them report their income or other payments accurately to the IRS. If we’re working with an S-Corporation or C-Corporation and they request a completed Form W-9, it’s crucial to comply with their requirement.
These scenarios represent common situations where Form W-9 is required, but there may be other instances specific to certain industries or contractual relationships. It’s important to understand the nature of our work or business relationships to determine if Form W-9 is necessary.
Obtaining and Submitting Form W-9
Methods of Obtaining Form W-9: There are multiple ways to obtain Form W-9. The easiest method is to download it directly from the IRS website (www.irs.gov) as it’s readily available in a printable format. Alternatively, we can request a copy from the entity that requires it, as they may have the form readily accessible.
Completing Form W-9: When completing Form W-9, we need to provide accurate and up-to-date information. We must enter our legal name or business name, the correct taxpayer identification number (TIN), and our address. It’s essential to review the instructions provided with the form to ensure we complete it correctly.
Submitting Form W-9 to Requesting Parties: Once we’ve completed Form W-9, we need to submit it to the requesting party or entity. They may have specific instructions on how to submit the form, such as mailing it or submitting it electronically. It’s crucial to follow their instructions to ensure proper delivery.
Remember, accuracy and timely submission of Form W-9 are vital. By providing the requested information promptly and correctly, we help the requesting party fulfill their reporting obligations, maintain compliance with tax regulations, and avoid potential penalties.
Key Components of Form W-9
Form W-9 consists of several important components that gather the necessary information for tax reporting. Here are the key components:
-
- Personal Information: This section collects details such as the recipient’s name, business name (if applicable), address, and other contact information. It is essential to provide accurate and up-to-date information in this section.
-
- Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN): The TIN section requires the recipient to provide their taxpayer identification number. For most individuals, this will be their Social Security Number (SSN). For businesses or entities, it will be their Employer Identification Number (EIN).
-
- Certification Section: This section includes certification statements that the recipient must sign. It confirms the accuracy of the provided TIN and whether the recipient is subject to backup withholding. It is crucial to review these statements carefully and certify them accurately.
Understanding these key components will help us navigate the sections of Form W-9 effectively and provide the necessary information required by the requester.
The Information Requested on Form W-9
Now that we know the basics, it’s time to examine the specific information requested on Form W-9. We’ll go through each section, including personal information like our name, business name, taxpayer identification number (TIN), and address. We’ll also look at the certification section, covering the correct TIN certification and exemptions from backup withholding.
Personal Information
The first section of Form W-9 requires us to provide our personal information. This includes our name, which should be the name associated with our tax records. If we’re operating a business under a separate name, we’ll also need to provide our business name. Make sure to enter the names exactly as they appear on our tax documents to avoid any discrepancies.
Next, we’ll come across the taxpayer identification number (TIN) field. For most individuals, this will be their Social Security Number (SSN). If we’re completing the form on behalf of a business or entity, we’ll need to provide the Employer Identification Number (EIN) associated with that organization. Double-check that we enter the correct TIN to prevent any processing issues.
Finally, we’ll need to provide our address. This should be the address where we currently reside or the address associated with our business. Ensure the address is complete and accurate, including the street name, city, state, and ZIP code. Providing the correct address helps in ensuring that any necessary communications or documents reach us without any complications.
Certification Section
The certification section of Form W-9 is crucial as it pertains to the accuracy of the information provided. Here, we’ll find two key components: the certification of the correct TIN and exemptions from backup withholding.
In the first part, we’ll need to certify that the TIN we provided is correct. It’s essential to double-check this information before certifying to avoid any potential problems down the line. Providing an incorrect TIN may result in issues with tax reporting and compliance.
The second part deals with exemptions from backup withholding. Backup withholding is a tax withheld by the payer if the payee fails to provide a correct TIN or doesn’t certify their exemption status. If we believe we’re exempt from backup withholding, we’ll need to indicate the appropriate exemption reason code. It’s crucial to understand the eligibility requirements for exemption and select the correct code accordingly.
By accurately completing the personal information and certification sections of Form W-9, we ensure that the requester has the necessary details to fulfill their reporting requirements, and we maintain compliance with tax regulations.
When and How to Use Form W-9
Let’s explore when and how to use Form W-9. Understanding the scenarios that require Form W-9 is crucial, such as for independent contractors, freelancers, partnerships, LLCs, S-Corporations, and C-Corporations. We’ll also cover the methods of obtaining Form W-9, completing the form accurately, and submitting it to the requesting parties. So, let’s dive in!
Scenarios Requiring Form W-9
-
- Independent Contractors: If you work as an independent contractor, clients may request you to complete Form W-9. They need your taxpayer identification information to accurately report the payments they made to you. As an independent contractor, you have the freedom to choose your clients and work on a project basis.
-
- Freelancers and Self-Employed Individuals: Similar to independent contractors, freelancers and self-employed individuals may be asked to complete Form W-9. Whether you’re a freelance writer, graphic designer, or consultant, clients or businesses that pay for your services may require your completed Form W-9.
-
- Partnerships and LLCs: Partnerships and Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) may require partners or members to complete Form W-9. This enables them to report the income distributed to partners or members accurately. If you’re part of a partnership or LLC, they may ask you to provide a completed Form W-9.
-
- S-Corporations and C-Corporations: S-Corporations and C-Corporations often need to collect Form W-9 from individuals or entities they make payments to. This helps them report income or other payments accurately to the IRS. If you work with an S-Corporation or C-Corporation and they request a completed Form W-9, it’s important to comply with their requirement.
These scenarios represent common situations where Form W-9 is required, but there may be other specific instances depending on your industry or contractual relationships. It’s essential to understand the nature of your work or business relationships to determine if Form W-9 is necessary.
Obtaining and Submitting Form W-9
Methods of Obtaining Form W-9: There are a few ways to obtain Form W-9. The most convenient method is to download it directly from the IRS website (www.irs.gov), where it’s available in a printable format. Alternatively, the entity requesting the form may provide you with a copy as they likely have the form readily accessible.
Completing Form W-9: When completing Form W-9, accuracy is key. Provide your legal name or business name, the correct taxpayer identification number (TIN), and your address. Take the time to review the instructions provided with the form to ensure you complete it correctly.
Submitting Form W-9 to Requesting Parties: Once you’ve completed Form W-9, you’ll need to submit it to the requesting party or entity. They may provide specific instructions on how to submit the form, such as mailing it or submitting it electronically. Make sure to follow their instructions carefully to ensure proper delivery.
Implications of Form W-9 in Accounting
Let’s explore the implications of Form W-9 in accounting. Understanding its role in income reporting, tax compliance, and the responsibilities of both the recipient and the requesting party is crucial. So, let’s dive in!
Role of Form W-9 in Income Reporting
Form W-9 plays a vital role in income reporting. It allows the recipient to provide their taxpayer identification information to the requesting party. This information helps the requesting party accurately report the income they have paid to the recipient. By matching the income reported by the payer with the income reported by the recipient, Form W-9 ensures consistency and transparency in the tax system.
Tax Reporting and Compliance
Form W-9 is an essential tool for tax reporting and compliance. When the recipient completes and submits Form W-9, they ensure that their income is properly reported. By providing accurate taxpayer identification information, the recipient maintains their own tax compliance and helps the requesting party fulfill their reporting obligations.
It’s important for the recipient to accurately complete Form W-9 to ensure that their income is correctly reported on their individual tax returns. Failing to provide accurate information or refusing to complete Form W-9 can have serious implications, such as backup withholding or potential penalties for non-compliance.
Implications for Requesting Parties
For the requesting parties, obtaining a completed Form W-9 is crucial to fulfill their reporting obligations. It allows them to accurately report the payments made to the recipient, track income, and ensure compliance with tax regulations. Requesting parties have a responsibility to collect and retain Form W-9 from the recipients as supporting documentation for their tax reporting.
Failure by the requesting party to collect or retain Form W-9 can lead to potential penalties or challenges in accurately reporting income. It’s in the best interest of the requesting party to obtain and securely store the completed Form W-9 to demonstrate compliance with tax requirements.
Understanding the implications of Form W-9 in accounting is important for both the recipients and the requesting parties. Accurate completion and submission of Form W-9 ensure proper income reporting, facilitate tax compliance, and maintain transparency in the tax system. By fulfilling their respective responsibilities, both parties contribute to the integrity and effectiveness of the accounting process.
Common Misconceptions about Form W-9
There are a few common misconceptions surrounding Form W-9 that I would like to address. Firstly, many people mistakenly believe that completing a Form W-9 determines their employment status. However, this is not the case. The purpose of Form W-9 is to provide your taxpayer identification number (TIN) to the entity that is requesting it, whether you are an employee or an independent contractor.
Secondly, another misconception is that filling out a Form W-9 initiates tax withholding. In reality, the form itself does not trigger any tax withholding. The withholding of taxes typically occurs when you receive payments, and the payer is required to withhold taxes based on your tax status and the amount being paid.
Lastly, it is a common myth that Form W-9 is only required for U.S. citizens. In fact, this form is used to collect TIN information from both U.S. citizens and resident aliens. Nonresident aliens, on the other hand, are generally required to fill out Form W-8BEN or W-8BEN-E instead.
Form W-9 vs. Form W-4: Understanding the Difference
Alright, let’s dive into the difference between Form W-9 and Form W-4. When it comes to Form W-4, it’s all about your employer and your withholding allowances. This form is used to determine how much income tax should be withheld from your paycheck based on your filing status, dependents, and other factors.
On the other hand, Form W-9 is a whole different ball game. This form is not for your employer, but rather for businesses or individuals who need your taxpayer identification number (TIN) for reporting purposes. It’s like giving them your tax ID so they can accurately report any payments made to you.
Now, there may be situations where you need to fill out both forms. For instance, if you’re starting a new job, you’ll likely need to complete a Form W-4 for your employer to set up your tax withholding. At the same time, if you’re working as an independent contractor or providing services to other businesses, they may ask you to fill out a Form W-9 to collect your TIN for reporting their payments to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Who can request Form W-9?
Any individual or entity that needs to collect taxpayer identification information for reporting purposes can request Form W-9. This includes businesses, organizations, partnerships, LLCs, and other entities that make payments subject to reporting requirements.
Is Form W-9 required for foreign contractors?
Yes, Form W-9 is required for foreign contractors if they receive payments from U.S. entities or individuals that are subject to reporting requirements. Foreign contractors must provide the necessary taxpayer identification information to ensure accurate reporting of income.
What happens if I refuse to complete Form W-9?
If you refuse to complete Form W-9 when requested by the payer, the payer may be required by the IRS to withhold a specific percentage of your payments as backup withholding. This withholding is done to ensure compliance with tax regulations and may have implications for both the payer and the recipient.
Can I amend or update Form W-9?
No, once you have submitted Form W-9 to the requesting party, you cannot amend or update the form. However, if your information changes (such as your name, TIN, or address), it is your responsibility to provide the updated information to the payer. You may need to complete a new Form W-9 with the updated details.
Tips for Accurate Form W-9 Completion
Now that we’ve covered the basics of Form W-9, it’s essential to focus on ensuring accuracy when completing the form. Here are some helpful tips that will assist both you and me in accurately completing Form W-9.
Double-Checking Information
When filling out Form W-9, it’s crucial to double-check the information provided. Ensure that the name, business name (if applicable), taxpayer identification number (TIN), and address are all entered correctly. Even a small mistake in these details can lead to issues with tax reporting and compliance. Taking a few extra moments to review the information can save us from potential headaches down the road.
Maintaining Up-to-Date Records
It’s important to keep our records up to date and ensure that the information provided on Form W-9 reflects our current status. If any changes occur in our name, TIN, or address, it’s our responsibility to update this information promptly. By maintaining accurate and up-to-date records, we can avoid any confusion or discrepancies when it comes to tax reporting and compliance.
Seeking Professional Guidance
If we have any doubts or questions regarding Form W-9, it’s always wise to seek professional guidance. Tax laws and regulations can be complex, and it’s perfectly understandable to seek assistance from a tax professional or accountant. They can provide expert advice tailored to our specific situation, ensuring that we complete Form W-9 accurately and comply with all the necessary requirements.
Remember, accuracy is crucial when it comes to Form W-9. By double-checking the information, maintaining up-to-date records, and seeking professional guidance when needed, we can ensure a smooth and accurate completion process.
Appendices:
Appendix A
Appendix B
The IRS has some handy resources to help with Form W-9:
- About Form W-9, Request for Taxpayer Identification Number and Certification | Internal Revenue Service
- How to complete Form W-9 – Tax
- 2018-2023 Form IRS W-9 Fill Online, Printable, Fillable, Blank – pdfFiller
- How to Fill Out a W-9 for Nonprofits | Step-by-Step Guide – Donorbox
Appendix C
Glossary of Terms
Form W-9: A tax form issued by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in the United States. It is used to request the taxpayer identification information of individuals or entities that are required to file an information return with the IRS. Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN): A unique identification number used by the IRS to track taxpayers and their tax obligations. It can be an individual’s Social Security Number (SSN) or an Employer Identification Number (EIN) for businesses. Backup Withholding: A withholding tax imposed by the IRS on certain payments to ensure tax compliance. It is typically withheld at a flat rate of 24% and applies to individuals or entities that fail to provide a correct TIN or fail to certify exemption from backup withholding. Independent Contractor: An individual or entity engaged in a trade or business who provides services to another entity but is not an employee. Independent contractors are typically responsible for their own taxes and are not subject to tax withholding by the entity receiving their services. Freelancer: An individual who offers their services on a project or task basis, often in a self-employed capacity. Freelancers are typically not employees and are responsible for their own taxes and reporting their income. Partnership: A business structure where two or more individuals or entities come together to carry on a trade or business for profit. Each partner contributes to the business’s operation and shares in its profits and losses. Limited Liability Company (LLC): A hybrid business entity that combines elements of a corporation and a partnership. LLCs provide limited liability protection to their owners (known as members) while allowing flexibility in taxation and management. S-Corporation: A type of corporation that elects to pass corporate income, losses, deductions, and credits through to its shareholders for federal tax purposes. This allows shareholders to report the income and losses on their individual tax returns. C-Corporation: A standard corporation that is treated as a separate legal entity from its owners (shareholders). C-corporations are subject to corporate tax on their profits and can be subject to double taxation if profits are distributed to shareholders as dividends. Income Reporting: The process of reporting and disclosing taxable income to the IRS on various tax forms, such as Form W-9, Form 1099, or Form 1040, depending on the individual or entity’s tax obligations. Tax Compliance: The act of complying with tax laws and regulations by accurately reporting income, claiming eligible deductions and credits, and paying the appropriate amount of tax owed. Employment Status: The classification of an individual’s relationship with an employer, determining whether they are an employee or an independent contractor. Employment status affects tax obligations, benefit eligibility, and legal rights and protections.